Dependent Parallel Approaches
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

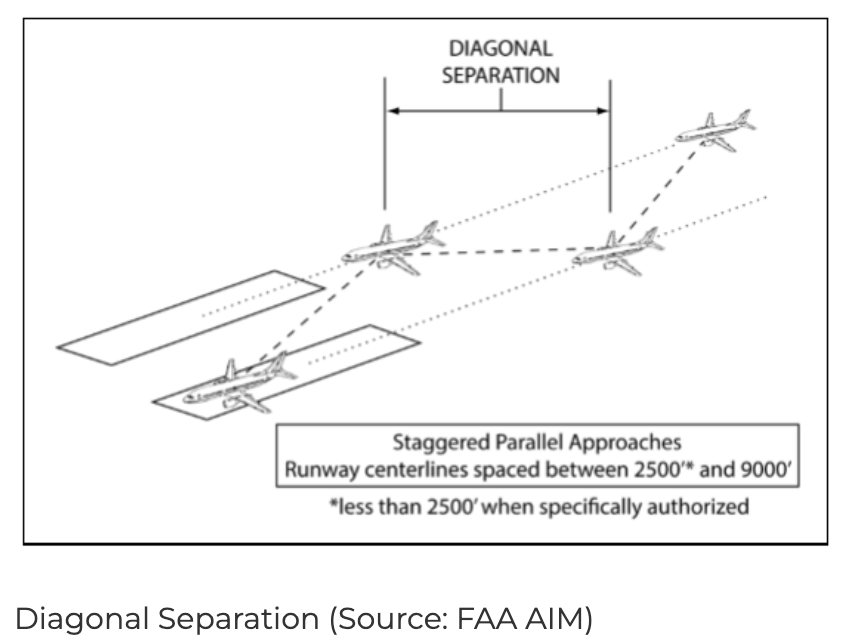
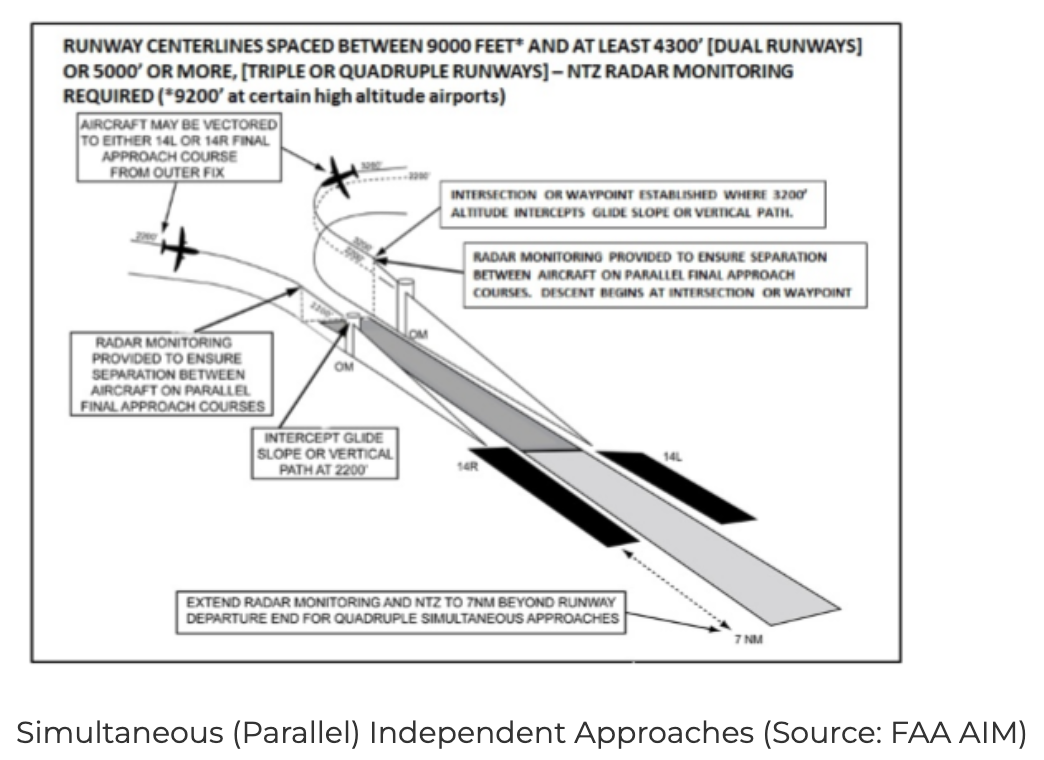
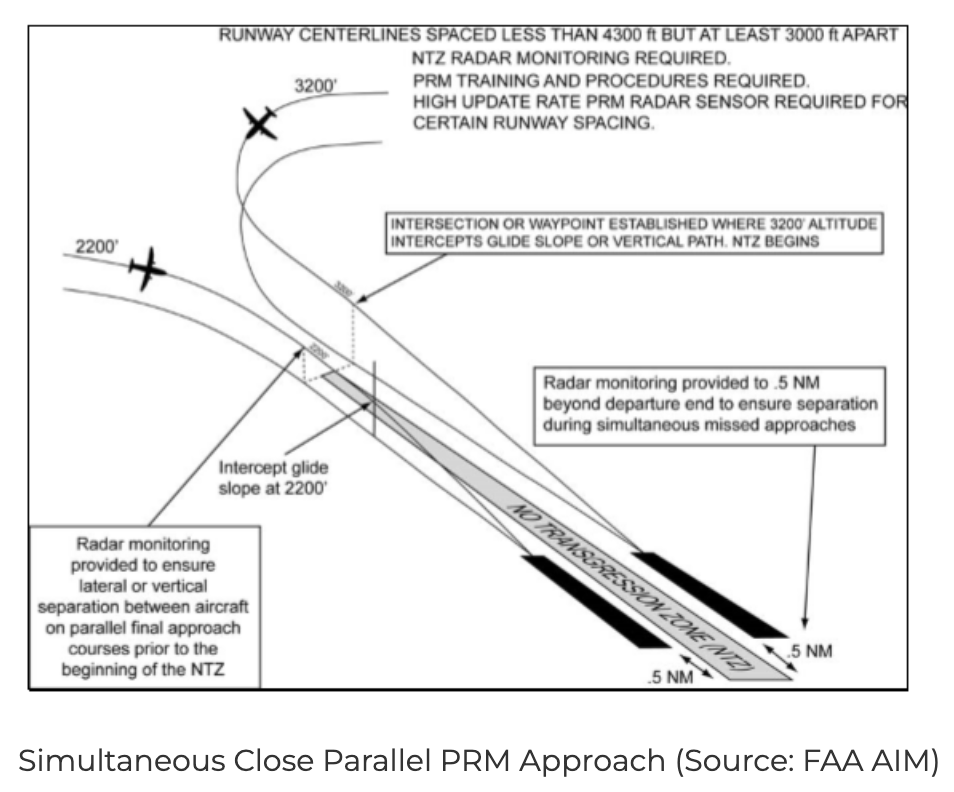
Dependent parallel approaches are instrument procedure operations used at airports with multiple parallel runways. These procedures allow air traffic controllers to sequence arriving aircraft on adjacent runways simultaneously—but unlike independent parallel approaches, strict longitudinal and diagonal separation standards must be maintained.
Key Characteristics
- Operational Dependency Aircraft are not separated independently but instead require controlled spacing in terms of both time and distance to ensure safety. A minimum of 1.0 NM diagonal spacing is typically required, although this can vary based on airport layout, runway orientation, and aircraft category.
- Controller Monitoring Air traffic controllers are actively involved in ensuring spacing is maintained throughout the final approach, especially from the final approach fix (FAF) to the runway threshold.
- Visual and Instrument Support: These operations often rely on high-fidelity radar systems, PAPI (Precision Approach Path Indicators), and other navigational aids to facilitate accurate tracking and timely intervention.
Implementation Context
- High-Volume Airports Frequently used at capacity-heavy airports like ATL (Atlanta), DFW (Dallas/Fort Worth), and ORD (Chicago O'Hare), especially when demand for simultaneous arrivals is high.
- Peak Period Utility Particularly beneficial during rush hours, weather disruptions, or runway maintenance, when maintaining throughput without sacrificing safety is crucial.
- Benefits vs. Independent Approaches While independent parallel approaches permit aircraft to land without coordination across runways, dependent operations allow increased efficiency while using fewer navigational resources. However, they demand precise spacing compliance, making controller skill and pilot awareness essential.
Why It Matters to Safety
- Separation Assurance Aids in maintaining collision-free approach paths.
- Efficiency Optimization Increases arrival rate without exceeding workload thresholds for ATC.
- Conflict Avoidance Reduces the potential for runway incursions or missed approaches due to unexpected aircraft convergence.
Categories:
- Dependent Parallel Approaches
- Parallel Runway Operations
- Instrument Flight Procedures
- IFR Arrivals
- Approach and Landing
- Simultaneous Operations
- FAA Terminal Procedures
- Controlled Airspace Management
- Runway Separation Requirements
- Radar Vectoring Techniques
- Final Approach Monitoring
- Obstacle Clearance Procedures
- Staggered Approach Spacing
- Wake Turbulence Avoidance
- Air Traffic Flow Management
- Terminal Maneuvering Area
- Independent vs Dependent Approaches
- Precision Approach Monitoring
- ATC Separation Standards
- Instrument Landing Systems
- Aircraft Sequencing Procedures
- Flight Path Deconfliction
- High Density Traffic Operations
- Surveillance Technology in ATC
- Runway Utilization Optimization
- Capacity Management in Terminal Areas
- IFR Procedure Design
- FAA Order 7110.65
- Airspace Complexity Factors
- Final Approach Fix Strategy
- Flight Risk Management
- Controller Workload Balancing
- Visual Approach Alternatives
- ATC Phraseology
- Navigation System Accuracy
- Multiple Runway Integration
- Airport Arrival Efficiency
- Operational Safety Margins
- Dynamic Spacing Tools
- Pilot-Controller Communication
- Aviation Safety X
- ASXWiki
- Pages with math render errors
