Jet Exhaust Nozzle
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Jet Exhaust Nozzle
A jet exhaust nozzle is a specially shaped tube at the rear of a jet engine that accelerates the exhaust gases, converting them into a high-velocity jet that produces thrust.
Function
The primary function of a jet exhaust nozzle is to:
- Generate thrust: By accelerating the exhaust gases, the nozzle creates the force needed to propel the aircraft forward.
- Conduct exhaust gases: The nozzle directs the exhaust gases to the free stream, ensuring they are expelled efficiently.
- Set mass flow rate: The nozzle's design and area determine the amount of exhaust gases that flow through the engine, which in turn affects the overall thrust.
Location
The nozzle is located downstream of the power turbine, the final stage of the jet engine.
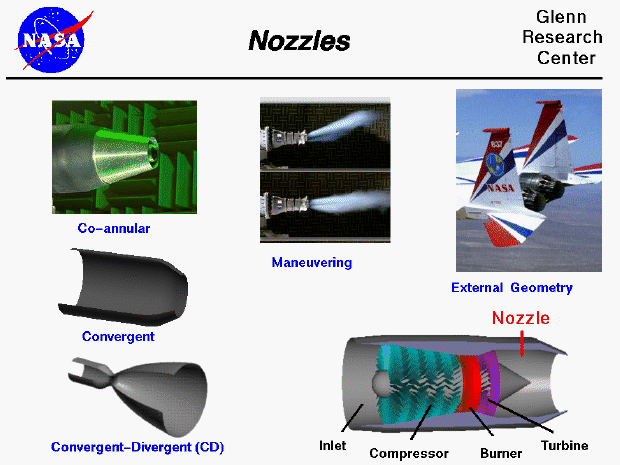
Design
- Nozzles come in various shapes and sizes depending on the type of engine and the aircraft's mission.
- Simple turbojets and turboprops often use fixed geometry convergent nozzles.
- Turbofan engines may use co-annular nozzles, where the core flow exits the center nozzle and the fan flow exits the annular nozzle.
- Afterburning turbojets and turbofans require variable geometry convergent-divergent (CD) nozzles.
Materials
Aircraft exhaust nozzles are typically made of heat-resistant materials like titanium, which can withstand the high temperatures and pressures of the exhaust gases.
