Kilohertz (kHz) in Aviation Communication
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Kilohertz (kHz) in Aviation Communication
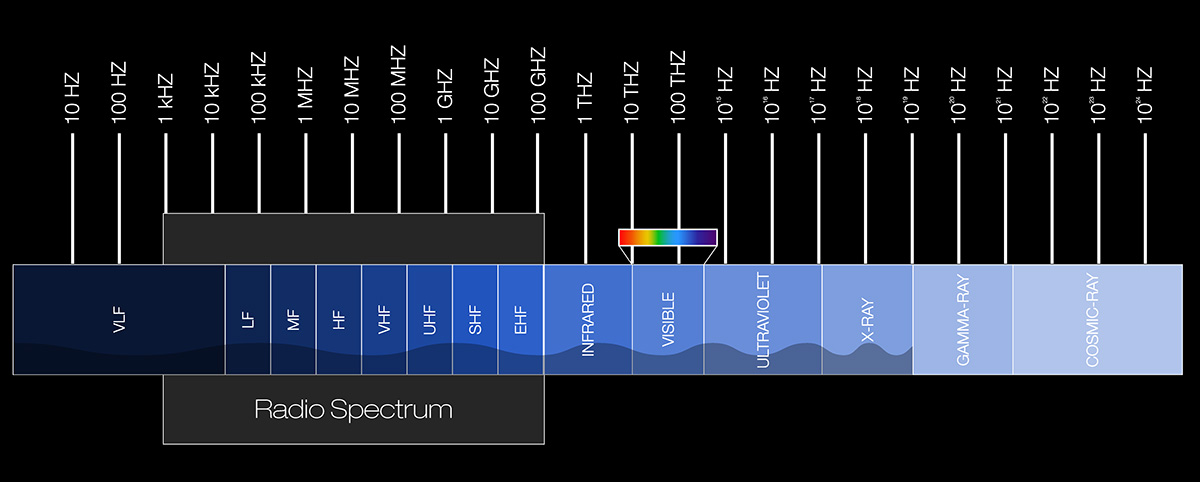
In aviation, kilohertz (kHz) is a standard unit of frequency equal to 1,000 hertz. It plays a crucial role in defining the operating frequencies of aviation communication systems, especially in the VHF (Very High Frequency) and HF (High Frequency) bands.
Use in Aviation
Kilohertz is commonly used to specify communication frequencies for:
- HF communications: Generally used for long-distance and transoceanic flights, where VHF line-of-sight limitations are impractical. These frequencies are typically listed in kilohertz (e.g., 5,598 kHz).
- VHF communications: While frequencies in this band are often expressed in megahertz (MHz), the actual increments and channel spacings (e.g., 25 kHz or 8.33 kHz spacing) are derived from kilohertz-level resolution.
Importance
- Ensures accurate tuning between pilots and air traffic control (ATC) for safe and coordinated communication.
- Plays a key role in navigation systems such as NDBs (Non-Directional Beacons), which transmit in the LF/MF bands measured in kilohertz.
- Standardized frequency assignments help avoid interference and support international aviation operations.
Related Units
- Hertz (Hz): The base unit of frequency.
- Megahertz (MHz): Equal to 1,000 kilohertz, often used for VHF communication listings.
Example Frequencies
- HF ATC Channel: 5,598 kHz (used in oceanic control sectors)
- NDB Navigation: Typically operates between 190 – 535 kHz
- VHF Comm Channels: 118.000 MHz – 136.975 MHz (spacing based on kilohertz resolution)
